
This paper presents evidence in support of the myosin hypothesis for selective dendritic transport.įarías, G. Differential trafficking of transport vesicles contributes to the localization of dendritic proteins. The role of selective transport in neuronal protein sorting. Arf family G proteins and their regulators: roles in membrane transport, development and disease. Role of rab GTPases in membrane traffic and cell physiology.
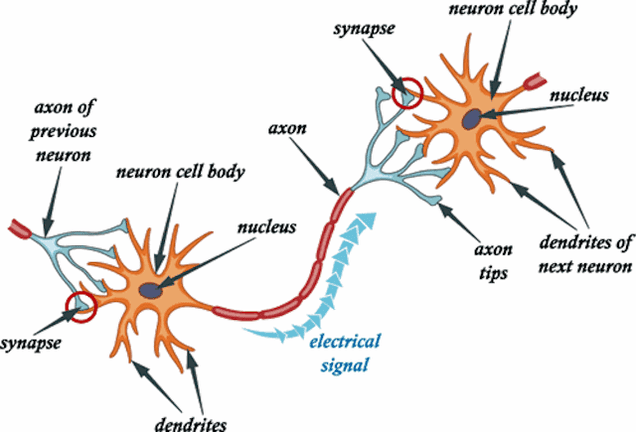
Linking molecular motors to membrane cargo. Multiple modes of cytoplasmic dynein regulation. Kinesin superfamily motor proteins and intracellular transport. The molecular motor toolbox for intracellular transport. Role of vesicle tethering factors in the ER–Golgi membrane traffic. Protein sorting at the trans-Golgi network. Impaired intracellular trafficking defines early Parkinson's disease. Axonal transport and neurodegenerative disease. Biophysical challenges to axonal transport: motor-cargo deficiencies and neurodegeneration. Hereditary spastic paraplegias: membrane traffic and the motor pathway. Seeing the unseen: the hidden world of slow axonal transport. The Fine Structure of the Nervous System: The Neurons and Supporting Cells (Oxford Univ. Almost nothing is yet known about these links.Ĭraig, A. There must be links between the process of protein sorting, which determines the cargoes present in a vesicle and hence the identity of a vesicle, and the recruitment of the correct motors, SNAREs (soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptors) and tethers, which determine the fate of a vesicle. The basis for selective transport depends on the regulation of motor proteins, but the underlying mechanisms remain controversial. Selective microtubule-based transport is crucial for the targeting of both axonal and dendritic proteins. By contrast, little is known about the mechanisms underlying axonal protein sorting. Some of the sorting signals and sorting adaptors that mediate the targeting of dendritic proteins have been identified. Selective sorting, selective transport and selective delivery are the key events for maintaining neuronal polarity. Nearly every aspect of neuronal function depends on the accurate localization of polarized membrane proteins to the axon or dendrites.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
